

If the above settings are pushed via GPO – it requires some time to applied to the destinations computers. Also, you can create default rules which allows everything.įollowing “Script Rules” screenshot shows the same BAT file “TestBATScript.bat” is allowed on the %OSDRIVE% which is the “C:\Scripts” for users and denied on the “E:\Scripts\” for everyone. Script rules options are same as the executable rules – Publisher, Path and File Hash along with Allow or Deny. Interestingly the same variable “%PROGRAMFILES%” returns both “C:\Program Files\” & “C:\Program Files (x86)”.įollowing screenshot example shows default “Executable rules” which permits everything along with a rule to deny “Google Chrome” for everyone including Administrators deny overrides other options. I prefer this.Įxecutable Rules based on “ File hash” – this is for application which are not sighed.Įxample screenshot of “Executable Rules” – in this example users (everyone) are allowed ONLY to execute “7-Zip” and “Notepad++” which are installed within “C:\Program Files\” or “C:\Program Files (86)\” whereas “Administrators” can execute all there is a “Deny” by default for rest.
APPLOCKER SERVICE WINDOWS 8 SOFTWARE
Set allow or deny action to executable application here few options available here –Įxecutable Rules based on “ Publisher” – allow all signed software by authorised publisher.Įxecutable Rules based on “ Path” – allow specific file or folder. “Audit only” – this setting does not prevent execution rather it generates audit logs only about what items are executed on the Windows OS and who executed it.
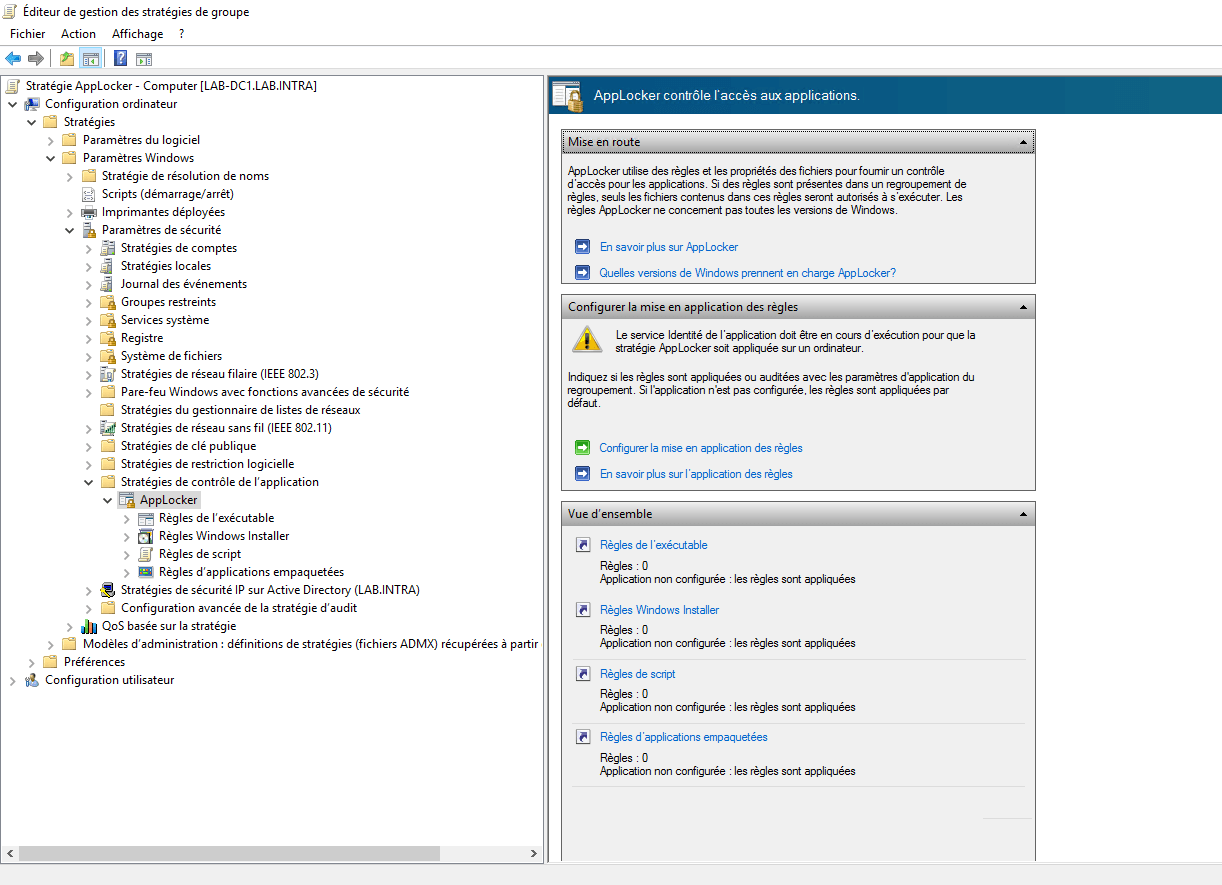
“Scripts rules” are applied to all scripts available on the Windows OS. “Executable rules” are applied to application programs installed on the Windows OS. Enforcement rule enforces “allow” and “deny” operations. Right click on the AppLocker -> go to Properties -> Select “Enforcement rules” for both Executables and Scripts. In an ideal environment all the AppLocker settings should combines into a single Group Policy Object (GPO) and pushed onto computers via Active Directory. Step2: Setup Application Whitelisting using “Local Group Policy Editor” or “Group Policy Management Console”ĪppLocker settings are available within “Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Application Control Policies -> AppLocker”. Without AppIDSvc AppLocker is unable to determine and verify application, scripts, installers and executables. Step1: Start the “Application Identity” (AppIDSvc) service & set to start automaticĪppIDSvc service is a Microsoft service used by AppLocker to determine and verify the identity of an application. Part 1 – Setting up the Application Whitelisting on Windows application whitelisting logs showing which apps are allowed, which are denied, who executed the app, when, from where etc).
APPLOCKER SERVICE WINDOWS 8 HOW TO
Part 2 – this discuss technical steps regarding how to get visibility, analytics and alerts about the application whitelisting using Splunk (e.g. Part 1 – this discuss technical steps regarding how to setup application whitelisting on Windows platform and push the settings to bunch of windows computers.
I will discuss setting up Splunk for AppLocker, so that we get real time visibility/analytics of application whitelisting and alerting. Application whitelisting is the solution that allows execution of pre-approved apps and scripts only and disallow rest.Īpplication whitelisting can be done using many tools – in this example I will discuss how to get application whitelisting done using in-build Windows tools I will use Windows AppLocker utility to implement application whitelisting. If you familiar with security compliance requirements such as PCI DSS or HIPAA – one of the requirements is “application whitelisting”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
